Showing posts with label SAP Beginners. Show all posts
Showing posts with label SAP Beginners. Show all posts
what is unicode and non-unicode system in SAP
Unknown
Unicode : Multi language support
Non Unicode : single language support
Unicode supports all multiple languages like english, chainaa, german,..etc.
Nonunicode :only supports two languages i.e english and german.
After NetWeaver and ECC 5.0 and etc. supports unicode kernel.
Unicode provides a unique number for every character, no matter what the platform, no matter what the program, no matter what the language.
OLD Code pages have the following disadvantages!
* Unicode is mandatory for SAP systems deploying JAVA applications.
* Many companies are adopting service oriented architecture standards providing
web services to enable global interoperability. these standards require Unicode.
Non Unicode : single language support
Unicode supports all multiple languages like english, chainaa, german,..etc.
Nonunicode :only supports two languages i.e english and german.
After NetWeaver and ECC 5.0 and etc. supports unicode kernel.
Unicode provides a unique number for every character, no matter what the platform, no matter what the program, no matter what the language.
OLD Code pages have the following disadvantages!
- They cover only a subset of all characters.
- Different codepages have incompatibilities between each other.
- Data exchange is restricted between code pages. there are simply to many code pages.
- Unicode has the cabaility to support all the languages in the world in one code page!
- it support 65,000 characters and has room to support an additional 1 million characters.
* Unicode is mandatory for SAP systems deploying JAVA applications.
* Many companies are adopting service oriented architecture standards providing
web services to enable global interoperability. these standards require Unicode.
7:34 PM
BASIS
,
SAP Beginners
Start & Stop SAP System in UNIX, Linux OS Environment
Unknown
Starting the SAP System
1. Log on in your OS level as a user with SAP administrator authorization (<SID>adm).
2. Enter the command startsap [DB|R3|ALL]. The following applies to this command:
• DB starts the database system:
|
• R3 starts the instances & associated processes of the SAP System:
|
• ALL starts both the database system & the SAP System:
|
Stopping the SAP System
1. Log on in your OS level as a user with SAP administrator authorization (<SID>adm).
2. Enter the command stopsap [DB|R3|ALL]. The following applies to this command:
• DB stops the database system:
|
• R3 stops the instances & associated processes of the SAP System:
|
• ALL stops both the database system & the SAP System.
|
7:07 PM
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
,
Sybase
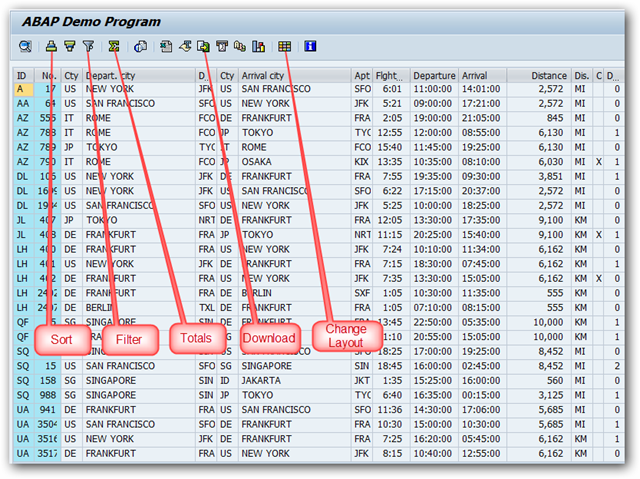
What is SAP ALV?
Unknown
ALV stands for ABAP List Viewer. ALV gives us a standard List format and user interface to all our ABAP reports. ALV is created by a set of standard function modules provided by SAP.
ALV provides a lot of inbuilt functions to our reports and some of the functions are listed below.
- Sorting of records
- Filtering of records
- Totals and Sub-totals
- Download the report output to Excel/HTML
- Changing the order of the columns in the report
- Hide the unwanted columns from the report
Because of the above functions, ALV substantially decreases the report development time. ALV takes care of rendering the list and we can concentrate only on the data retrieval part.
Some of the function modules used to create ALV reports are listed below.
| FUNCTION MODULE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| REUSE_ALV_LIST_DISPLAY | Display an ALV list |
| REUSE_ALV_GRID_DISPLAY | Display an ALV grid |
| REUSE_ALV_COMMENTARY_WRITE | Output List header information |
| REUSE_ALV_VARIANT_F4 | Display variant selection dialog box |
| REUSE_ALV_VARIANT_EXISTENCE | Checks whether a variant exists |
| REUSE_ALV_FIELDCATALOG_MERGE | Create field catalog from dictionary structure or internal table |
Simple ALV report.
DATA: it_spfli TYPE TABLE OF spfli.
SELECT * FROM spfli INTO TABLE it_spfli.
CALL FUNCTION 'REUSE_ALV_GRID_DISPLAY'
EXPORTING
i_structure_name = 'SPFLI'
TABLES
t_outtab = it_spfli.
Simple ALV Output List
7:53 PM
ABAP
,
SAP Beginners
SAP Transport Return Code Status
Unknown
RC = 0, successfully imported.
RC = 4, imported ended with warning.
Common issue:
• Generation of programs and screens
• Columns missing and Rows missing.
Common issue:
• Generation of programs and screens
• Columns missing and Rows missing.
RC = 8, not imported ended with error
Common issue:
• Syntax error.
• Program generation error.
• Dictionary activation error.
• Method execution error.
Common issue:
• Syntax error.
• Program generation error.
• Dictionary activation error.
• Method execution error.
RC = 12, import is cancelled.
Common issue:
• Import is canceled due to object missing.
• Objects are not active.
• Program terminated due to job “RDDEXECL” is not working.
• Connection problem between system.
Common issue:
• Import is canceled due to object missing.
• Objects are not active.
• Program terminated due to job “RDDEXECL” is not working.
• Connection problem between system.
RC = 16, import is cancelled.
Common issue:
• Import cancelled due to system down while importing.
• Import cancelled due to user expires while importing
• Import cancelled due to insufficient roles.
Common issue:
• Import cancelled due to system down while importing.
• Import cancelled due to user expires while importing
• Import cancelled due to insufficient roles.
12:30 PM
BASIS
,
SAP Beginners
How to change the default SAP GUI client number
Unknown
You need to change an instance profile parameter on the R/3 system.
Goto :TCODE RZ10,
Goto :TCODE RZ10,
login/system_client The default value is 000.
Which Client you want change client value like 300,800,000,.
5:27 PM
BASIS
,
SAP Beginners
How to increase Dialog work process time in SAP
Unknown
Goto transaction code RZ11, enter the parameter name – rdisp/max_wprun_time and press enter. Once you get the below screen, click on Change Value and enter the desired time. Please not to set the value to 0 as it will make the running time unlimited.
No restart required as the parameter is dynamically switchable. For permanent change, please do it on transaction code RZ10. You can refer to SAP Note 25528.
No restart required as the parameter is dynamically switchable. For permanent change, please do it on transaction code RZ10. You can refer to SAP Note 25528.
4:46 PM
BASIS
,
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
How to Modify SAP Transport Number Range
Unknown
You want to change the transport number range on the SAP System.
SAP stored the last transport request in the table E070L. You can find the information using transaction code SE16 or SE16N.
Due to non-modifiable function on transaction code SE16/SE16N, you may need to update the table from database level. Below example is on Oracle database. If let say, the latest transport number from table E070L is SIDK800111 and you wanted to change to SIDK000121.
4:40 PM
ABAP
,
BASIS
,
SAP Beginners
SAP Kernel Up-gradation in Windows Environment step by step
Unknown
Step by Step Procedure for Kernel Up-gradation:
- Basis Administrator shall login to www.service.sap.com with OSS & password and download the latest Kernel files.
- Downloads---->SAP Support Packages---->Support packages & Patches-Entry By application group---->SAP application Components---->SAP ERP---->SAP ERP 6.0----> Entry By Component---->SAP ECC Server----> SAP KERNEL 7.20 EXT 64-BIT UC---->Windows Server on X64 64BIT---->MaxDB “SAPEXEDB_402-20006745.SAR” (Kernel Part II)
- Downloads---->SAP Support Package---->Support packages & Patches-Entry By application group---->SAP application Components---->SAP ERP---->SAP ERP 6.0---->Entry By Component---->SAP ECC Server---->SAP SAP KERNEL 7.20 EXT 64-BIT UC---->Windows Server on X64 64BIT---->#Database Independent “SAPEXE_402-20006748.SAR” (Kernel Part I).
2. Login to the Server through OS level with SIDadm.
3. Make the copies of the existing folders in the backup folder :-
- Drive:\usr\sap\SID\SYS\exe
4. Stop the SAP Instance & Services
- SAPSID_00
- SAPSID_01
- SAPHostControl
- SAPHostExec
5. Extract the SAR Files
- Go to command prompt
- Go to as above path & Extract the files
c:\sapcar –xvf *.sar
6. Copy and paste the uncared files to \usr\sap\SID\SYS\exe\uc\NTAMD64\ .
7. Select the option copy and Replace if it prompts pop message as “There is already a file with same name in the location.”
8. Start the services and Instances
9. Check the updated kernel from Command Prompt by giving disp+work.
9:26 AM
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
How to generate SAP Solution Manager Key
Unknown
To Generate Solution Manager Key Execute T-code SMSY in
Solution Manager system, you need to do the following steps:
1) Create a system by right clicking on System entry and select Create new system.
1) Create a system by right clicking on System entry and select Create new system.
2) Enter the System Name i.e., SID (3 chars)
3) Product = SAP ECC (select from the list)
4) Product Version= ECC 5.0 (select from the list)
5) Save the entries.
6) Select Menu Item "System--->Other Configuration" and enter the SID which you have created earlier.
7) Enter the Server Name(hostname)
8) Finally click on Generate "Installation/Upgrade Key Button "
The system generates a Key ,copy that Key and paste it in the SAPINST screen when it prompts for Sol man Key.
6:38 PM
ABAP
,
BASIS
,
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
SAP Security Audit Log
Unknown
The Security Audit Log is a tool designed for auditors who
need to take a detailed look at what occurs in the SAP system. By activating
the audit log, you keep record of those activities you consider relevant for
auditing. This information is recorded on a daily basis in an audit file on
each application server. You can then access this information for evaluation in
the form of an audit analysis report. Statistical information can easily be
retrieved on transactions and reports.
The audit log’s main objective is to record:
·
Security-related
changes to the SAP System environment
(for example, changes to user master records)
(for example, changes to user master records)
·
Information that
provides a higher level of transparency
(for example, successful and unsuccessful logon attempts)
(for example, successful and unsuccessful logon attempts)
·
Information that
enables the reconstruction of a series of events
(for example, successful or unsuccessful transaction starts)
(for example, successful or unsuccessful transaction starts)
Specifically, you can record the following
information in the Security Audit Log:
- Successful
and unsuccessful dialog logon attempts
- Successful
and unsuccessful RFC logon attempts
- RFC
calls to function modules
- Successful
and unsuccessful transaction starts
- Successful
and unsuccessful report starts
- Changes
to user master records
- Changes
to the audit configuration
To Configure the audit log : SM19
To Analysis audit log : SM20
To Delete old log : SM18
Before you activate the audit log you have to setup several
parameters in RZ10
:
rsau/enable :
Set to 1 to activates audit logging
rsau/local/file : Name and location of the audit log
file
rsau/max_diskspace/local :
Max. space of the audit file. If maximum size is reached auditing stops.
rsau/selection_slots : Max. number of filters
rsau/max_diskspace/local : Max. space of the audit file. If
maximum size is reached auditingstops.
rsau/max_diskspace/per_file : minimum is 1MB & Maximum is 2 GB
rsau/max_diskspace/per_day : minimum
value should be 3*per_file & maximum 1024 GB.Socheck
these parameter.
2:21 PM
BASIS
,
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
How extract a SAR file in SAP
Unknown
What is a SAR file ?
SAR files are delivered by SAP for releasing supportpackages of Kernel and other OS level binaries.
How to extract a SAR file in SAP
Navigate to the path where the SAR file is located and use following command
to extract a SAR file.
SAPCAR -xvf <filename.SAR>
6:29 PM
BASIS
,
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
How to Kill the Work Process in SAP SM50
Unknown
Stopping Run-Away or “Bad” Work Processes
1. Log on to any client in the appropriate SAP system.
2. Go to transaction SM50.
3. On the Process Overview screen, find the process which must be stopped. Place a √ in the □ to the left of the process number to be stopped by pressing Space.
On the top-most menu bar,click the Process → Cancel without core.
4. Click the blue arrow circle picture-icon to refresh the Process
Overview screen until the stopped process has cleared from the
display.
5. You may now leave the SM50 transaction.
If this does not kill the process, you can go to transaction SM04 and kill the
user’s session. If this does not kill the process, you can log on to the server,
open a Task Manager session, and End the Process. If this does not kill the
session, there is an executable in the RUN directory on the server called
sapntkill.exe. Run it providing the process ID number. If none of the above work,
you have no choice but to “bounce” the SAP instance and/or possibly the serve.
10:15 AM
BASIS
,
BASIS BASIC
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Utility Commands
Unknown
DB2 Utility Commands
List
the running utilities and their progress
db2
list utilities show detail
Throttle
a running utility.
First
find the Utility ID.
db2
list utilities show detail
Throttle
the utility to a value of 1 to 10. 10 being the most throttled.
db2
set UTIL_IMPACT_PRIORITY for <util_id> TO 5
8:52 AM
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Tuning Commands
Unknown
DB2 Tuning Commands
Quickly
look at some basic tuning measurements
db2
"select db_name, rows_read, rows_selected, lock_waits,
lock_wait_time, deadlocks, lock_escals, total_sorts, total_sort_time
from table (snapshot_database (' ', -1) ) as snapshot_database"
8:51 AM
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Tablespace and Bufferpool Commands
Unknown
DB2 Tablespace and Bufferpool Commands
View
the names, pagesize, and number of pages of the bufferpools in your
database
db2
"select bpname,pagesize,npages from syscat.bufferpools"
Make
a bufferpool resize automatically. You must have STMM turned on at
the database configuration level
db2
alter bufferpool bp1 size AUTOMATIC
Alter
a bufferpool size that is a fixed size
db2
ALTER BUFFERPOOL IBMDEFAULTBP SIZE 15000;
Add
space to a DMS tablespace
db2
"alter tablespace <tblspace> extend (all 8000)"
8:49 AM
ABAP
,
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Table and Index Commands
Unknown
DB2 Table and Index Commands
Look
at columns and data types of a table
db2
describe table schema.tabelename
Look
at one column's data type.
db2
"describe select <colname> from schema.tablename"
Look
at indexes on a table
db2
describe indexes for table schema.tablename
Export
data to a file in ixf format
db2
export to tablename.ixf of ixf messages tablename.txt select * from
SCHEMA.TABNAME
Import
data from an ixf file
db2
import from filename.ixf of ixf messages tablename.txt insert into
SCHEMA.TABNAME
Import
using Load which is faster (doesn't check constraints) and
NONRECOVERABLE doesn't log anything
db2
load from filename.ixf of ixf insert into SCHEMA.TABNAME
nonrecoverable;
Build
a file to set integrity on all tables that are in set integrity
pending state
db2
"select 'set integrity for '||tabschema||'.'||tabname ||'
immediate checked;' from syscat.tables where type = 'T' and status =
'C'" > file.out
8:48 AM
ABAP
,
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Security Commands
Unknown
DB2 Security Commands
Build
a script to grant user execute privilege on all packages.
db2
"select 'db2 grant execute on package
'||pkgschema||'.'||pkgname||' to user <user>;' from
syscat.packages where pkgschema = 'NULLID'" > output.file
Security
Notes
dbadm
auth must be revoked before any other database privlege
create_not_fenced_routine
must be revoked before create_external_routine
8:46 AM
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Backup and Restore Commands
Unknown
DB2 Backup and Restore Commands
Take
an OFFLINE backup
db2
connect to <dbname>
db2
quiesce database immediate force connections
db2
connect reset
db2
backup database <dbname> to <path> compress without
prompting
after
backup completes:
db2
connect to <dbname>
db2
unquiesce database
db2
connect reset
Take
an ONLINE Backup
db2
backup db <dbname> to <path> online compress
or
use a background process on a linux/unix machine
nohup
db2 backup db <dbname> to <path> online compress &
List
recent backups and where they are stored
db2
list history backup all for <dbname>
Check
the integrity of a backup image
db2ckbkp
<image name>
Restore
from Incremental Backup Automatic
db2
restore db <dbname> incremental automatic taken at <timestamp>
If
you need to restore an incremental backup manually this command will
give you the required previous backups.
db2ckrst
-d <dbname> -t <timestamp of image>
8:44 AM
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
DB2 Commands Home
Unknown
Basic Commands
Size
of your database :
db2
'call get_dbsize_info(?,?,?,0)'
Version
of DB2 you are running:
db2level
Stop
the db2 instance:
db2stop
Stop
an instance that has current connections
db2
force applications all
db2
deactivate db <dbname>
db2
terminate
db2stop
force
ipclean
Start
the db2 instance:
db2start
Kill
a hung instance (last resort):
db2_kill
-all
List
the databases in an instance:
db2
list db directory
List
the cataloged nodes:
db2
list node directory
Show
the database manager configuration settings:
db2
get dbm cfg
Show
the database level configuration settings:
db2
get db cfg for <dbname>
Activate
a database:
db2
activate db <dbname>
Deactivate
a database:
db2
deactivate db <dbname>
View
the DB2 License:
db2licm
-l
To
switch between partitions:
db2
terminate; export DB2NODE=<new-node-num>
8:41 AM
BASIS
,
DB2
,
MSSQL
,
SAP Beginners
Subscribe to:
Comments
(
Atom
)